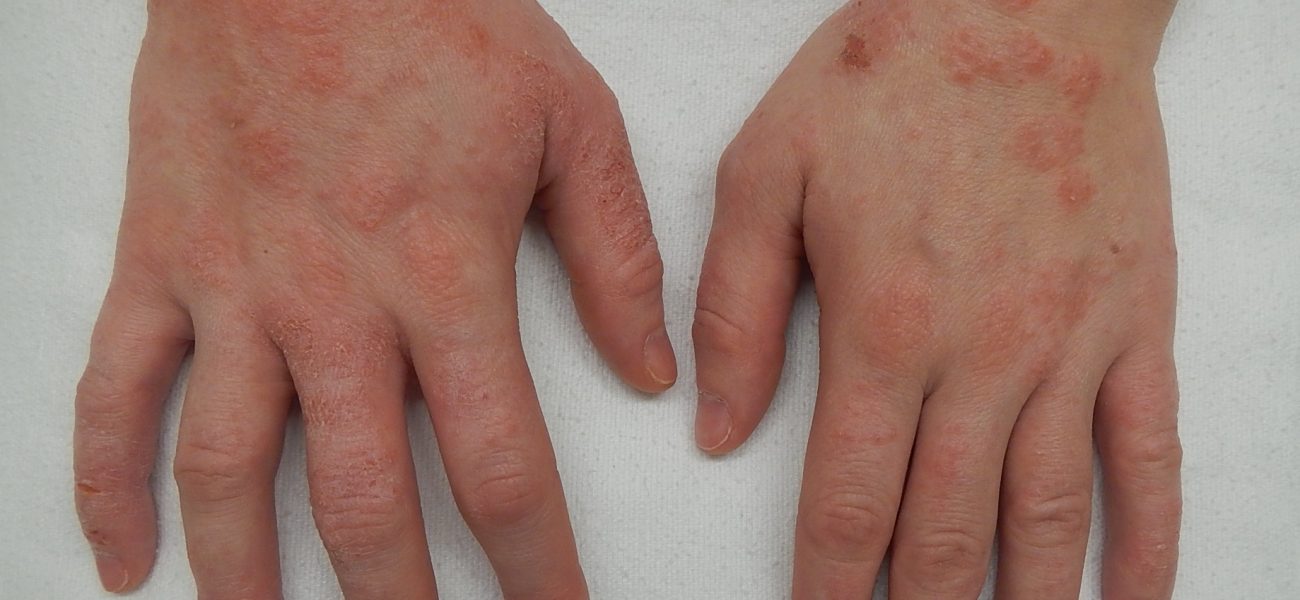
Eczema is a condition in which patches of skin become inflamed, itchy, cracked, and rough. Some types can also cause blisters.
Different types and stages of eczema affect 31.6 million people in the United States, which equals more than 10% of the population.
Many people use the word eczema when referring to atopic dermatitis, which is the most common type. The term atopic refers to a collection of conditions that involve the immune system, including atopic dermatitis, asthma, and hay fever. The word dermatitis refers to inflammation of the skin.
Certain foods, such as nuts and dairy, can trigger symptoms of eczema. Environmental triggers can include smoke, pollen, soaps, and fragrances. Eczema is not contagious.
About a quarter of children in the U.S. have the condition, as well as 10% of African Americans, 13% of Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders, 13% of Native Americans, and 11% of people who are white.
Some people outgrow the condition, while others will continue to have it throughout adulthood. This article will explain what eczema is and discuss its symptoms, treatments, causes, and types.
Causes
Researchers do not know the definitive cause of eczema, but many health professionals believe that it develops from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Children are more likely to develop eczema if a parent has it or another atopic condition. If both parents have an atopic condition, the risk is even higher.
Some environmental factors may also bring out the symptoms of eczema. These include:
- Irritants: These include soaps, detergents, shampoos, disinfectants, juices from fresh fruits, meats, and vegetables.
- Allergens: Dust mites, pets, pollens, and mold can all lead to eczema. This is known as allergic eczema.
- Microbes: These include bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, viruses, and certain fungi.
- Hot and cold temperatures: Very hot and very cold weather, high and low humidity, and perspiration from exercise can bring out eczema.
- Foods: Dairy products, eggs, nuts and seeds, soy products, and wheat can cause eczema flares.
- Stress: This is not a direct cause of eczema, but it can make the symptoms worse.
- Hormones: Females may experience increased eczema symptoms when their hormone levels are changing, such as during pregnancy and at certain points in the menstrual cycle.
General eczema symptoms
In most cases eczema symptoms are mild. The most common symptoms of atopic dermatitis include:
- dry, scaly skin
- skin flushing
- itching
- open, crusted, or weeping sores
People with severe eczema may need more intensive treatment to relieve their symptoms. Continuous rubbing and scratching can also lead to skin infections.
Treatments
There is currently no cure for eczema. Treatment for the condition aims to heal the affected skin and prevent flares of symptoms.
Doctors will suggest a treatment plan based on an individual’s age, symptoms, and current state of health.
For some people, eczema goes away over time. For others, however, it is a lifelong condition.
The sections below will list some treatment options.
The list of some Hereditary Angioedema medicine:
Rutinib Cream