Breast cancer is a disease in which cells in the breast increasing out of monitoring. There are different kinds of breast cancer. The kind of breast cancer rely on which cells in the breast turn into cancer.
Breast cancer can upcoming in different parts of the breast. A breast is created of three main parts: lobules, ducts, and connective tissue. The lobules are the cheek that produce milk. The ducts are tubes that bearing milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which consists of fibrous and fatty tissue) shut in and holds everything together. Most breast cancers initiate in the ducts or lobules.
Breast cancer can expansion outside the breast through blood vessels and lymph vessels. When breast cancer expansion to other parts of the body, it is said to have metastasized.
Where breast cancer starts
Breast cancers can begin from different parts of the breast. The breast is an body that sits on top of the upper ribs and chest muscles. There is a left and right breast and every one has mainly glands, ducts, and fatty tissue. In women, the breast makes and delivers milk to feed new-borns and infants. The amount of fatty tissue in the breast determines the size of every breast.
The breast has different parts:
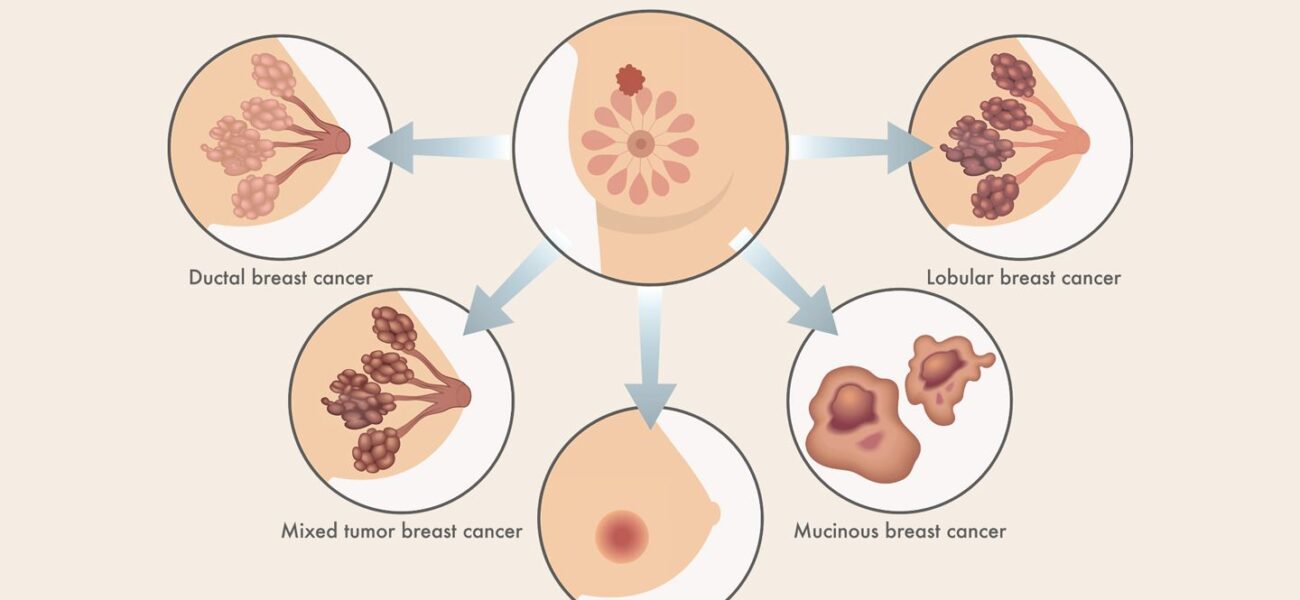
Lobules are the glands that make breast milk. Cancers that start here are called lobular cancers.
Ducts are small canals that come out from the lobules and carry the milk to the nipple. This is the most common place for breast cancer to start. Cancers that start here are called ductal cancers.
The nipple is the opening in the skin of the breast where the ducts come together and turn into larger ducts so the milk can leave the breast. The nipple is encompassed by slightly darker thicker skin called the areola. A less common type of breast cancer called Paget disorder of the breast can begin in the nipple.
The fat and connective tissue (stroma) encompassed the ducts and lobules and help keep them in place. A less common type of breast cancer called phyllodes tumor can begin in the stroma.Blood vessels and lymph vessels are also found in each breast. Angiosarcoma is a less common type of breast cancer that can start in the lining of these vessels. The lymph system is described below.
A small number of cancers start in other tissues in the breast. These cancers are called sarcomas and lymphomas and are not really thought of as breast cancers.
How breast cancer spreads
Breast cancer can expansion when the cancer cells get into the blood or serum system and then are carried to other parts of the body.
The lymph (or lymphatic) system is a part of your body’s immune system. It is a network of lymph nodes (small, bean-sized glands), ducts or vessels, and organs that work together to collect and carry clear lymph fluid through the body tissues to the blood. The clear lymph fluid inside the lymph vessels contains tissue by-products and waste material, as well as immune system cells.
The lymph vessels carry lymph fluid away from the breast. In the case of breast cancer, cancer cells can enter those lymph vessels and start to grow in lymph nodes. Most of the lymph vessels of the breast drain into:
Lymph nodes under the arm (axillary lymph nodes)
Lymph nodes inside the chest near the breastbone (internal mammary lymph nodes)
Lymph nodes around the collar bone (supraclavicular [above the collar bone] and infraclavicular [below the collar bone] lymph nodes)
If cancer cells have spread to your lymph nodes, there is a higher chance that the cells could have traveled through the lymph system and spread (metastasized) to other parts of your body. Still, not all women with cancer cells in their lymph nodes develop metastases, and some women with no cancer cells in their lymph nodes might develop metastases later.
Types of breast cancer
There are many different types of breast cancer. The type is determined by the specific kind of cells in the breast that are affected. Most breast cancers are carcinomas. The most common breast cancers such as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and invasive carcinoma are adenocarcinomas, since the cancers start in the gland cells in the milk ducts or the lobules (milk-producing glands). Other kinds of cancers can grow in the breast, like angiosarcoma or sarcoma, but are not considered breast cancer since they start in different cells of the breast. Breast cancers are also classified by certain types of proteins or genes each cancer might make. After a biopsy is done, breast cancer cells are tested for proteins called estrogen receptors and progesterone receptors, and the HER2 gene or protein. The tumor cells are also closely looked at in the lab to find out what grade it is. The specific proteins found and the tumor grade can help decide the stage of the cancer and treatment options.
How Is Breast Cancer Treated?
Breast cancer is treated in several ways. It depends on the type of breast cancer and how far it has growth. People with breast cancer constantly get further than one kind of treatment.
Surgery. An operation where croakers cut out cancer tissue.
Chemotherapy. Using special drugs to shrink or kill the cancer cells. The medicines can be capsules you take or drugs given in your veins, or occasionally both.
Hormonal remedy. Blocks cancer cells from receive the hormones they need to grow.
Biological remedy. Workshop with your body’s vulnerable system to help it fight cancer cells or to control side goods from other cancer treatments.
Radiation remedy. Using high- energy shafts ( analogous toX-rays) to kill the cancer cells.
Doctors from different specialties frequently work together to treat breast cancer. Surgeons are doctors who perform operations. Medical oncologists are doctors who handle cancer with drug. Radiation oncologists are doctors who treat cancer with radiation.
The list of some breast cancer medicine:
Tucaxen
Afanix
Cykin
Tysinor
Lapacent
Latinib
Lapacent
Inpoza
Hertinib
Hernix
Parib
Olanib
Juparib
Palbocent
Palbonix
Palboxen