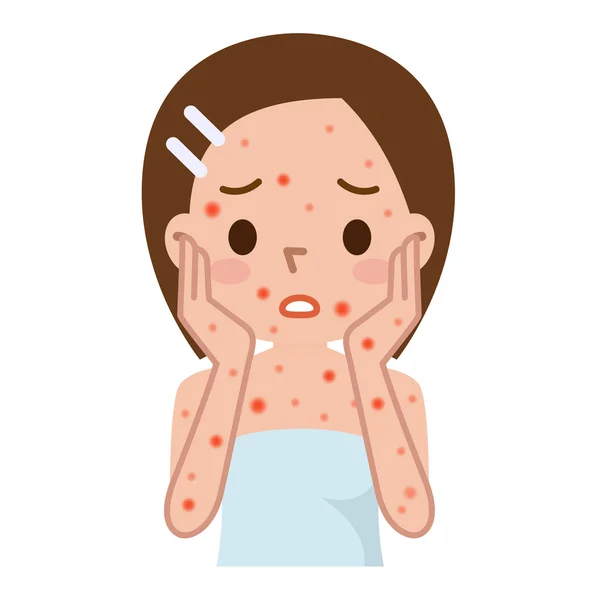
A skin rash is a visible change in the skin’s color, texture, or appearance. It can affect any part of the body and may be accompanied by itching, pain, swelling, or other symptoms. A skin rash can have many different causes, ranging from mild to serious. In this blog post, we will explore some of the common types of skin rashes, their possible causes, and how to treat them effectively.
Types of Skin Rashes
There are many different types of skin rashes, depending on their appearance, location, and cause. Some of the common types are:
• Contact dermatitis. This is a type of allergic reaction that occurs when the skin comes into contact with a substance that it is sensitive to. The substance can be an allergen (such as poison ivy, nickel, or latex) or an irritant (such as soap, detergent, or perfume). The rash usually appears within hours or days of exposure and is often red, itchy, and blistered.
• Eczema. This is a chronic inflammatory condition that causes dry, itchy, and scaly patches of skin. It often affects people with a family history of allergies or asthma and can be triggered by stress, environmental factors, or certain foods. The rash usually appears on the face, neck, elbows, knees, or hands.
• Hives. These are raised, red, and itchy welts that appear on the skin due to an allergic reaction to something ingested or inhaled. They can vary in size and shape and may come and go within minutes or hours. The rash can be caused by foods (such as nuts, shellfish, or eggs), medications (such as antibiotics or aspirin), insect stings (such as bees or wasps), or infections (such as viral or bacterial).
• Psoriasis. This is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes thick, red, and scaly plaques of skin. It occurs when the immune system attacks healthy skin cells and causes them to grow faster than normal. The rash usually affects the scalp, elbows, knees, lower back, or genitals and can be associated with joint pain and nail changes.
• Viral rash. This is a rash that results from a viral infection that affects the skin. Some common viral infections that cause rashes are chickenpox (a contagious infection that causes fluid-filled blisters all over the body), measles (a highly contagious infection that causes fever and red spots on the face and body), and molluscum contagiosum (a mild infection that causes small, pearly bumps on the skin). Causes of Skin Rashes Skin rashes can have many different causes, depending on the type and location of the rash. Some of the possible causes are:
• Injury. Trauma to the skin from cuts, burns, scrapes, or bites can cause inflammation, infection, or scarring that can result in a rash.
• Infection. Bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites can invade the skin and cause rashes that may be red, warm, swollen, or pus-filled. Some examples of infections that cause rashes are impetigo (a bacterial infection that causes honey-colored crusts on the face), ringworm (a fungal infection that causes circular patches on the skin), and scabies (a parasitic infection that causes intense itching and burrows under the skin).
• Disease. Various diseases and conditions can affect the skin and cause rashes. Some examples are lupus (an autoimmune disease that causes a butterfly-shaped rash on the face), liver disease (a condition that affects the liver function and causes yellowing of the skin), and diabetes (a condition that affects the blood sugar levels and causes darkening of the skin folds).
• Allergy. A skin rash is a significant change in the color, texture, or appearance of the skin. The substance can be something ingested (such as food or medication), inhaled (such as pollen or dust), or contacted (such as latex or poison ivy). The rash can appear within minutes or hours of exposure and can be accompanied by other symptoms such as swelling, hives, or difficulty breathing.
Symptoms of Skin Rashes
Skin rash symptoms vary depending on the type and cause of the rash.
Some common symptoms that may accompany a skin rash are:
• Itching. The skin may feel irritated, scratchy, or prickly due to inflammation, infection, or allergy. Itching can worsen the rash by causing more damage to the skin barrier.
• Pain. The skin may feel sore, tender, or throbbing due to injury, infection, or inflammation. Pain can limit the movement and function of the affected area.
• Swelling. The skin may appear larger or puffy due to fluid accumulation or inflammation. Swelling can cause pressure on nearby nerves or blood vessels and affect sensation or circulation.
• Redness. The skin may become red or warm due to increased blood flow or infection. Redness can indicate inflammation, irritation, or allergy.
• Crepitus. The skin may make cracking, popping, or grinding sounds when moving due to friction between rough surfaces. Crepitus can indicate damage to the cartilage, bone, or joint.
Diagnosis of Skin Rashes
To diagnose the cause of a skin rash, a doctor will usually perform a physical examination and ask about the history and symptoms of the condition. The doctor may also order some tests to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other possible causes. Some of these tests are:
• Skin biopsy. This involves taking a small sample of skin from the affected area and examining it under a microscope or sending it to a laboratory for further testing. This can help identify the type and cause of inflammation, infection, or abnormality in the skin.
• Allergy test. This involves exposing the skin to small amounts of different substances that may trigger an allergic reaction and observing the response. This can help identify the specific allergens that cause the rash and guide the treatment and prevention strategies.
• Blood test. This involves drawing a sample of blood from a vein and measuring the levels of certain substances in the blood that may indicate inflammation, infection, autoimmunity, or metabolic disorders. Examples of blood tests include complete blood count (CBC), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP), rheumatoid factor (RF), antinuclear antibody (ANA), and liver function tests (LFTs).
Treatment of Skin Rashes
The treatment of a skin rash depends on its cause, severity, and impact on daily life. The main goals of treatment are to relieve symptoms, reduce inflammation, clear infection, and prevent complications. Some common treatments for skin rashes are:
• Medications. These can help reduce pain and inflammation in the skin. They can be taken orally, topically administered, or injected into the skin. Examples of medications include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen (Advil) or naproxen (Aleve), antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec), corticosteroids such as hydrocortisone cream or prednisone pills, antibiotics for bacterial infections, antivirals for viral infections, antifungals for fungal infections, antiparasitics for parasitic infections, immunosuppressants for autoimmune diseases, and biologics for psoriasis.
• Phototherapy. The skin is exposed to regulated doses of ultraviolet (UV) radiation in order to decrease inflammation and limit the formation of aberrant skin cells. It can be used for conditions such as eczema and psoriasis. Phototherapy can be done in a doctor’s office or at home with a special device.
• Surgery. This involves removing or destroying the affected skin tissue with a scalpel, laser, or liquid nitrogen. It can be used for conditions such as warts, moles, or skin cancer.
• Lifestyle changes. These can help prevent or manage skin rashes by avoiding triggers, improving hygiene, moisturizing the skin, and protecting the skin from sun damage. Some examples of lifestyle changes are wearing loose-fitting clothing made of natural fibers, using mild soap and water to wash the skin gently, applying emollients or creams to keep the skin hydrated, using sunscreen or clothing to shield the skin from UV rays, and managing stress levels.
Home Remedies for Skin Rashes
In addition to medical treatment, there are some home remedies that can help ease skin rashes and improve comfort. Some of these are:
• Cold compress. Applying a cold pack or ice wrapped in a towel to the affected area for 15 to 20 minutes several times a day can help numb the pain and reduce swelling. Do not apply ice directly to the skin or for longer than 20 minutes at a time, as this can cause frostbite or nerve damage.
• Oatmeal bath. Soaking in a tub of warm water mixed with colloidal oatmeal (finely ground oats) for 15 to 20 minutes can help soothe itching and inflammation. Oatmeal has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and moisturizing properties that can benefit the skin.
• Aloe vera gel. Applying pure aloe vera gel extracted from the plant’s leaves to the affected area can help heal and hydrate the skin. Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and wound-healing properties that can help with various skin conditions.
• Honey. Applying raw honey to the affected area can help prevent infection and speed up healing. Honey has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties that can benefit the skin.
• Tea tree oil. Applying diluted tea tree oil to the affected area can help treat fungal infections and reduce inflammation. Tea tree oil has antifungal, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties that can help with various skin conditions.
When to See a Doctor
Skin rashes are usually not a medical emergency, but they can be a sign of a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Some situations when it is advisable to see a doctor for a skin rash are:
• The rash is severe, sudden, or unexplained.
• The rash is accompanied by fever, chills, rash, weight loss, or other signs of infection or systemic illness.
• The rash is caused by an injury that results in bleeding, infection, or scarring.
• The rash persists for more than six weeks despite home remedies and OTC medications.
• The rash interferes with daily activities and quality of life.
Summary
Skin rash is a common complaint that can affect any part of the body and may be accompanied by itching, pain, swelling, or other symptoms. A skin rash can have many different causes, ranging from mild to serious. In this blog post, we explored some of the common types of skin rashes, their possible causes, and how to treat them effectively.