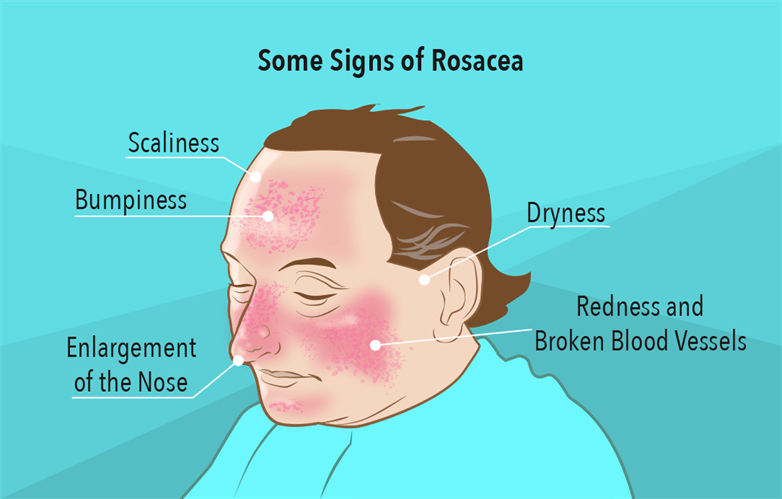
Flushing is a sensation of warmth and redness that usually affects the face, neck and chest. Flushing can occur for various reasons, such as emotions, temperature, food, alcohol, medications or medical conditions. Flushing is usually harmless and temporary, but it can sometimes be a sign of a more serious problem. In this blog post, we will discuss the causes, symptoms and treatment of flushing, as well as some tips on how to prevent and cope with it.
What causes flushing?
Flushing is caused by the dilation of the blood vessels under the skin, which increases blood flow and heat to the affected area. Flushing can be triggered by different factors, such as:
• Emotions: Flushing can occur when you feel strong emotions such as embarrassment, anger, anxiety or excitement. This is because emotions can activate the nervous system, which releases hormones that affect blood pressure and blood vessel dilation. Flushing due to emotions is also called blushing and it usually affects the face and neck.
• Temperature: Flushing can occur when you are exposed to heat or high humidity. This is because your body sweats to cool itself down and dilates the blood vessels to release heat. Flushing due to temperature is also called thermoregulatory flushing and it can affect any part of the body.
• Food: Flushing can occur when you eat certain foods that are hot, spicy or contain chemicals that affect blood vessels. Some of the common foods that can cause flushing are chili peppers, curry, garlic, cheese and chocolate. Flushing due to food is also called gustatory flushing and it usually affects the face and chest.
• Alcohol: Flushing can occur when you drink alcohol or have alcohol intolerance. This is because alcohol can affect the way your body metabolizes a substance called acetaldehyde, which causes blood vessel dilation and inflammation. Flushing due to alcohol is also called alcohol flush reaction and it usually affects the face, neck and chest.
• Medications: Flushing can occur when you take certain medications that have flushing as a side effect or interact with your body’s temperature regulation. Some of the common medications that can cause flushing are antibiotics, antihistamines, anticonvulsants, immunosuppressants, chemotherapy drugs and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
• Medical conditions: Flushing can occur when you have certain medical conditions that affect your hormones, blood pressure or blood vessels. Some of the common conditions that can cause flushing are menopause, hyperthyroidism, infections, fever, cancer, acromegaly, lymphoma, leukemia or malaria.
What are the symptoms of flushing?
The main symptom of flushing is having warmth and redness on your skin or clothes. Other symptoms may include:
• Sweating
• Itching
• Burning
• Tingling
• Headache
• Palpitations
• Nausea
• Dizziness
How is flushing diagnosed?
Flushing is usually diagnosed based on the history of symptoms and a physical examination. In some cases, additional tests may be needed to identify the cause of flushing or rule out other conditions. These tests may include:
• Blood tests: To check for signs of infection, inflammation, diabetes, thyroid problems, or hormonal imbalances.
• Urine tests: To check for signs of diabetes or kidney problems.
• Stool tests: To check for signs of intestinal infections or parasites.
• Chest X-rays: To check for signs of lung infections or pneumonia.
• CT scans or MRI scans: To check for signs of brain infections or tumors.
How is flushing treated?
The treatment of flushing depends on the cause and severity of the condition. Some general measures that can help with flushing include:
• Avoiding triggers: Avoiding factors that stimulate your blood vessels such as heat humidity, spicy foods, alcohol or stress can help reduce flushing.
• Practicing good hygiene: Washing your face and body with cool water and mild soap can help soothe your skin and remove sweat and bacteria that cause inflammation.
• Applying cold compresses: Applying cold compresses to your face and neck can help constrict your blood vessels and reduce heat and redness.
• Wearing loose clothing: Wearing loose clothing made of natural fabrics such as cotton or linen can help absorb sweat and keep you cool.
• Taking over-the-counter medications: Some medications such as aspirin or ibuprofen can help reduce inflammation and pain that may accompany flushing. However, these medications should not be used for more than two days without consulting your healthcare provider, as they may have side effects such as stomach bleeding, liver damage or kidney problems.
• Seeking medical attention: If your flushing is severe, persistent, or affects your quality of life, You should consult your doctor for additional evaluation and treatment. You may need medications that reduce the activity of your nervous system such as anticholinergics, beta-blockers or antidepressants. You may also need procedures that destroy or remove your blood vessels such as laser therapy, radiofrequency ablation or surgery.
How can flushing be prevented?
Some tips to prevent flushing include:
• Avoiding triggers: Avoiding factors that stimulate your blood vessels such as heat, humidity, spicy foods, alcohol or stress can help prevent flushing.
• Practicing good hygiene: Washing your face and body with cool water and mild soap can help prevent sweat and bacteria buildup that cause inflammation.
• Staying hydrated: Drinking enough fluids throughout the day can help regulate your body temperature and prevent dehydration which can cause flushing.
• Exercising moderately: Exercising regularly can help improve your blood circulation and metabolism which can prevent flushing. However, avoid exercising too intensely or too close to bedtime as this can increase your body temperature and stimulate flushing.
Conclusion
Flushing is a sensation of warmth and redness that usually affects the face neck and chest Flushing can occur for various reasons such as emotions temperature food alcohol medications medical conditions Flushing is usually harmless and temporary but it can sometimes be a sign of a more serious problem Flushing can also cause other symptoms such as sweating itching burning tingling headache palpitations nausea dizziness Flushing is usually diagnosed by taking your history and examining you In some cases additional tests may be needed Flushing is usually treated by avoiding triggers practicing good hygiene applying cold compresses wearing loose clothing taking over-the-counter medications seeking medical attention if needed Flushing can be prevented by avoiding triggers practicing good hygiene staying hydrated exercising moderately.