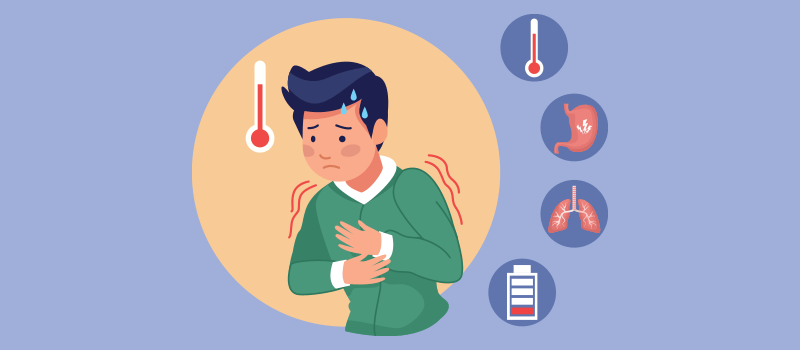
Fever is a common symptom that indicates your body is fighting an infection or another problem. It is not a disease by itself, but a sign of an underlying condition. Fever is usually measured by taking your body temperature with a thermometer. A normal body temperature is around 98.6°F (37°C), but it can vary slightly depending on the time of day, your age, your activity level and other factors. A fever is generally defined as a body temperature above 100.4°F (38°C). In this blog post, we will explain the causes, symptoms and treatment of fever, as well as some tips on how to prevent and manage it.
What causes fever?
Fever can be caused by many different factors, but the most common ones are:
• Infections: Bacteria, viruses and parasites can invade your body and trigger an immune response that raises your body temperature. Some of the most common infections that cause fever are colds, flu, ear infections, strep throat, bronchitis and urinary tract infections. These infections can spread through contact with infected people, animals or objects, or through contaminated food or water.
• Inflammation: Inflammation is a natural process that helps your body heal from injuries or diseases. However, sometimes inflammation can be excessive or chronic and cause fever. Some of the conditions that cause inflammation and fever are arthritis, lupus, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis and allergies.
• Medications: Some medications can have fever as a side effect or interact with your body’s temperature regulation. Some of the medications that can cause fever are antibiotics, antihistamines, anticonvulsants, immunosuppressants and chemotherapy drugs.
• Other causes: Fever can also be caused by other factors such as heat exhaustion, dehydration, hormonal changes, thyroid problems, cancer or blood clots.
What are the symptoms of fever?
The main symptom of fever is having a higher-than-normal body temperature. However, fever can also cause other symptoms such as:
• Chills and shivering
• Sweating
• Headache
• Muscle and joint pain
• Loss of appetite
• Fatigue
• Irritability
• Dehydration
• Confusion or delirium
How is fever diagnosed?
Fever is usually diagnosed by taking your body temperature with a thermometer. There are different types of thermometers available, such as oral, rectal, ear and forehead thermometers. Oral and rectal thermometers tend to be more accurate than ear and forehead thermometers. However, ear and forehead thermometers may be more convenient and comfortable to use. When you report your temperature to your healthcare provider, make sure you mention the type of thermometer you used and where you took the temperature (mouth, rectum, ear or forehead).
In some cases, your healthcare provider may also order some tests to find out the cause of your fever. These tests may include:
• Blood tests: To check for signs of infection, inflammation or dehydration.
• Urine tests: To check for urinary tract infections or kidney problems.
• Stool tests: To check for intestinal infections or parasites.
• Chest X-rays: To check for lung infections or pneumonia.
• CT scans or MRI scans: To check for brain infections or tumors.
How is fever treated?
The treatment of fever depends on the cause and severity of the condition. Some general measures that can help with fever include:
• Drinking plenty of fluids: This helps prevent dehydration and replace the fluids and electrolytes lost through sweating. Water, broth, juice or oral rehydration solutions are good choices. Avoid drinks that contain caffeine, alcohol or sugar as they can worsen dehydration or irritate your stomach.
• Eating light foods: This helps provide energy and nutrients to your body without causing nausea or indigestion. Foods such as crackers, toast, soup, yogurt, and fruits are easy to digest and can help soothe your stomach. Avoid foods that are spicy, fatty, fried, dairy, or high in fiber as they can aggravate your symptoms.
• Taking over-the-counter medications: Some medications such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil) can help lower your body temperature and relieve pain and inflammation. However, these medications should not be used for more than three days without consulting your healthcare provider, since they may have negative side effects such as liver damage stomach bleeding, or kidney problems. Children under the age of 18 should not be given aspirin. as it may cause a rare but serious condition called Reye’s syndrome.
• Seeking medical attention: If your fever is high (above 104°F or 40°C), persistent (more than three days), or accompanied by other symptoms such as severe headache, stiff neck, rash, chest pain, shortness of breath, or blood in urine or stool, You ought to get medical attention as soon as possible.
Antibiotics may be necessary if you are suffering from a bacterial infection. or other medications if you have an inflammatory or hormonal condition.
How can fever be prevented?
Some tips to prevent fever include:
• Practicing good hygiene: Washing your hands with soap and water before eating or preparing food,
after using the bathroom, and after touching sick people or animals can help prevent the spread of germs that cause infection.
• Getting vaccinated: Getting vaccinated against common diseases such as measles, mumps, rubella, chickenpox, flu, and pneumonia can help protect you from getting sick and developing fever.
• Avoiding contact with sick people: If someone in your household or workplace has a fever or an infection, try to avoid close contact with them until they recover. If you have to care for them, wear a mask, gloves, and wash your hands frequently.
• Staying hydrated: Drinking enough fluids throughout the day can help prevent dehydration and heat exhaustion, which can cause fever. Avoid exposure to extreme heat or sun without proper protection such as hats, sunglasses, and sunscreen.
Conclusion
Fever is a common symptom that indicates your body is fighting an infection or another problem. It is not a disease by itself but a sign of an underlying condition. Fever can be caused by many different factors such as infections inflammation medications or other causes. Fever can also cause other symptoms such as chills sweating headache pain and fatigue. Fever is usually diagnosed by taking your body temperature with a thermometer. Fever is usually treated by drinking plenty of fluids eating light foods taking over-the-counter medications seeking medical attention if needed. Fever can be prevented by practicing good hygiene getting vaccinated avoiding contact with sick people staying hydrated.
We hope this blog post has been informative and helpful for you. If you have any questions or comments about fever please feel free to leave them below.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions that people may have about fever:
Q: What is the difference between a fever and hyperthermia?
A: A fever is an increase in body temperature due to an infection or inflammation that stimulates the immune system. Hyperthermia is an increase in body temperature due to external factors such as heat exposure or drug overdose that overwhelm the body’s ability to regulate its temperature.
Q: How high is too high for a fever?
A: A fever above 104°F (40°C) is considered very high and may indicate a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. A fever above 107°F (41.7°C) is considered life-threatening and may cause brain damage or death.
Q: Can I take a bath or shower when I have a fever?
A: You can take a bath or shower when you have a fever if it makes you feel more comfortable. However, avoid using very hot or very cold water as it may worsen your symptoms or cause shock. Use lukewarm water and dry yourself well after bathing.
Q: Can I exercise when I have a fever?
A: You should avoid exercising when you have a fever as it may increase your body temperature further and dehydrate you more. Resting is the best way to recover from a fever. You can resume exercising when your fever goes away and you feel better.
Q: Can I drink alcohol when I have a fever?
A: You should avoid drinking alcohol when you have a fever as it may interfere with your medication lower your immune system dehydrate you more and worsen your symptoms. Drink plenty of water juice broth or oral rehydration solutions instead.