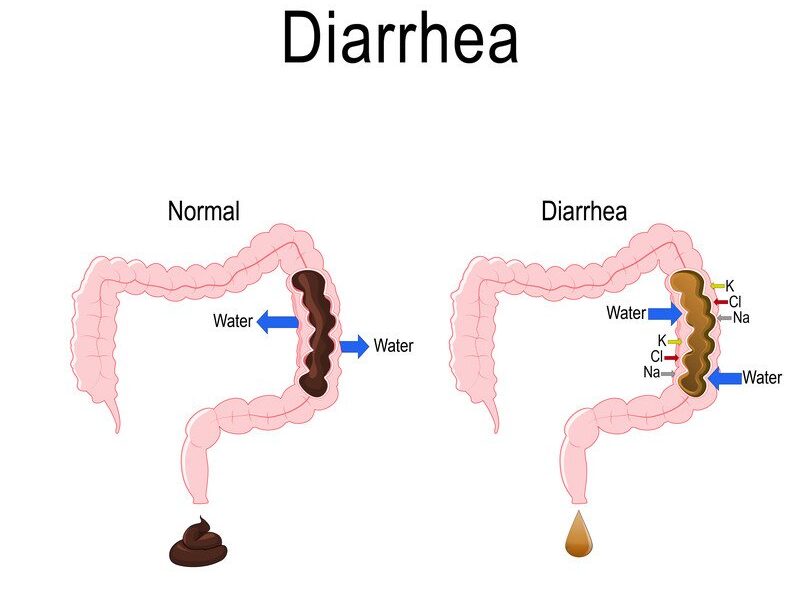
Diarrhea is characterized by loose, watery and frequent bowel movements that may be accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain or weight loss. Diarrhea can have various causes, ranging from infections and food intolerance to chronic diseases and medications. In most cases, diarrhea is mild and self-limiting, but sometimes it can be severe and require medical attention. In this blog post, we will discuss the causes, symptoms and treatment of diarrhea, as well as some tips on how to prevent it.
What causes diarrhea?
Diarrhea can be caused by many factors, but some of the most common ones are:
• Infections: Viruses, bacteria and parasites can infect the digestive tract and cause inflammation, irritation and increased fluid secretion. Some of the most common infectious agents that cause diarrhea are norovirus, rotavirus, salmonella, E. coli, campylobacter and giardia. These infections can be transmitted through contaminated food, water or contact with infected people or animals.
• Food intolerance: Some people may have difficulty digesting certain foods or ingredients, such as lactose, gluten, fructose or artificial sweeteners. This can result in gas, bloating and diarrhea after eating these foods. Food intolerance is different from food allergy, which involves an immune system reaction that can cause more serious symptoms such as hives, swelling and anaphylaxis.
• Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): IBS is a chronic condition that affects the function of the large intestine. It causes symptoms such as abdominal pain, cramping, bloating and changes in bowel habits, including diarrhea or constipation. The exact cause of IBS is unknown, but it may be related to stress, diet, hormones or genetics.
• Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): IBD is a group of chronic conditions that cause inflammation and ulcers in the lining of the digestive tract. IBD has two major forms: ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Both conditions can cause symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, bleeding, weight loss and fatigue. The exact cause of IBD is unknown, but it may be related to an abnormal immune system response to environmental or genetic factors.
• Medications: Some medications can have diarrhea as a side effect or interact with the normal bacteria in the gut. Some of the most common medications that can cause diarrhea are antibiotics, antacids, laxatives, chemotherapy drugs and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
• Other causes: Diarrhea can also be caused by other factors such as stress, anxiety, alcohol consumption, excessive caffeine intake, surgery, radiation therapy or certain diseases such as diabetes, hyperthyroidism or celiac disease.
What are the symptoms of diarrhea?
The main symptom of diarrhea is having loose, watery stools three or more times a day. Other symptoms may include:
• Urgency to go to the bathroom
• Abdominal pain or cramping
• Bloating or gas
• Nausea or vomiting
• Fever or chills
• Dehydration
• Blood or mucus in the stool
How is diarrhea diagnosed?
Diarrhea is usually diagnosed based on the history of symptoms and a physical examination. In some cases, additional tests may be needed to identify the cause of diarrhea or rule out other conditions. These tests may include:
• Stool culture: A sample of stool is sent to a laboratory to check for the presence of bacteria, viruses or parasites that may cause infection.
• Blood tests: A sample of blood is taken to check for signs of inflammation, infection or dehydration.
• Colonoscopy: A thin flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the anus to examine the inside of the colon and look for any abnormalities such as inflammation or ulcers.
• Imaging tests: X-rays, ultrasound or CT scans may be used to visualize the abdomen and look for any problems such as blockages or tumors.
How is diarrhea treated?
How to treat diarrhea varies according to its cause and how serious it is. Some general measures that can help with diarrhea include:
• Drinking plenty of fluids: This helps prevent dehydration and replace the fluids and electrolytes lost through diarrhea. Water, broth, sports drinks or oral rehydration solutions are good choices. Ignore drinks that contain caffeine, alcohol or sugar as they can worsen diarrhea.
• Eating bland foods: This helps reduce irritation and inflammation in the digestive tract. Foods such as bananas, rice, applesauce and toast are easy to digest and can help solidify stools. Avoid foods that are spicy, fatty, fried, dairy, or high in fiber as they can aggravate diarrhea.
• Taking over-the-counter medications: Some medications such as loperamide (Imodium) or bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) can help reduce the frequency and severity of diarrhea by slowing down the movement of the intestines or coating the lining of the stomach. However, these medications should not be used for more than two days without consulting a doctor, as they may mask the underlying cause of diarrhea or cause side effects such as constipation, drowsiness, or allergic reactions.
• Seeking medical attention: If diarrhea is severe, persistent, blood in stool, severe abdominal pain, thirst, dizziness, or reduced urine output), it is important to going to a doctor The doctor may prescribe antibiotics if an infection is suspected, or other medications such as steroids, immunosuppressants, or biologics if an inflammatory condition is diagnosed.
How can diarrhea be prevented?
Some tips to prevent diarrhea include:
• Practicing good hygiene: Washing hands with soap and water before eating or preparing food, after using the bathroom, and after touching animals can help prevent the spread of germs that cause infection.
• Drinking safe water: Using bottled water or boiling tap water before drinking or cooking can help avoid contamination by bacteria, viruses, or parasites.
• Eating safe food: Avoiding raw or undercooked meat, eggs, seafood, or dairy products can help prevent food poisoning by bacteria such as salmonella or E. coli. Also avoiding foods that are spoiled, moldy, or have been left out for too long can help prevent foodborne illness.
• Traveling wisely: When traveling to developing countries where sanitation standards may be low,
it is advisable to follow the advice above regarding water and food safety.
Also taking prophylactic antibiotics before traveling may help prevent traveler’s diarrhea caused by certain bacteria. However, only a doctor should approve this, as antibiotics can have side effects such as allergic reactions or resistance.
Conclusion
Diarrhea is a common condition that can have various causes and symptoms. It is usually mild and self-limiting but sometimes it can be severe and require medical attention. The treatment of diarrhea depends on the cause and severity of the condition but generally involves drinking plenty of fluids eating bland foods taking over-the-counter medications seeking medical attention if needed. Diarrhea can be prevented by practicing good hygiene drinking safe water eating safe food traveling wisely.